Abstract
Background: Autologous T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific for B-cell maturation antigen (CART-BCMA cells) show activity in refractory MM, but relapses remain common. Anti-PD-1 antibodies (Abs) augment CAR T cell activity pre-clinically, and induced CAR T cell re-expansion and responses in DLBCL patients progressing after CD19-specific CAR T cells (Chong et al, Blood 2017). The IMiDs lenalidomide (len) and pomalidomide (pom) may enhance efficacy, but also toxicity, of both CAR T cells and PD-1 inhibitors in MM. Elotuzumab (elo) has clinical anti-MM activity in combination with IMiDs and dexamethasone (dex), and synergizes with anti-PD-1 Ab in pre-clinical models.
Methods: We previously described outcomes of 25 subjects enrolled on our phase 1 study of CART-BCMA cells in relapsed/refractory MM (Cohen et al, ASH 2017, #505). We identified and retrospectively reviewed 5 subjects who progressed after CART-BCMA and received a PD-1 inhibitor (pembrolizumab (pembro)) combination as their next therapy. Responses were assessed by IMWG criteria. CART-BCMA levels were assessed by flow cytometry and qPCR pre-treatment, 2-4 weeks after first pembro dose, then q4 weeks until progression. Pembro dosing was 200mg every 3 weeks; dex dosing was 20-40mg/week.
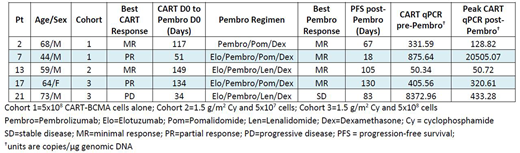
Results: Characteristics of the 5 subjects are in the Table. Median prior lines was 9; all had high-risk cytogenetics. All were refractory to pom, 2 to pembro/pom/dex, and 1 to elo. Best response to CART-BCMA was PR in 2, MR in 2, and PD in 1. Median time from CART-BCMA to pembro-based therapy was 117 days. All patients still had CART-BCMA cells detectable by qPCR, with 2 (pts. 07 and 21) still detectable by flow, at initiation of salvage therapy. The first pt. (02) received pembro/pom/dex and had MR but progressed at 2 months, with no detectable CART-BCMA re-expansion. The second pt. (07) had rapidly-progressing kappa light chain MM 2 months post-CART-BCMA and had previously progressed on pembro/pom/dex. He started elo/pembro/pom/dex and had MR at day 12 (free kappa 1446 to 937 mg/L), associated with robust expansion of CART-BCMA cells (875.64 to 20505.07 copies/µg DNA by qPCR; 0.7% to 6.4% of peripheral CD3+ cells by flow). Re-expanded CART-BCMA cells were predominantly CD8+ and highly activated (89% HLA-DR+, up from 18% pre-therapy). This response was short-lived, however, with progression 1 week later, and return of CART-BCMA levels to baseline at week 5. Three subsequent subjects then received elo/pembro/dex with either len or pom; with 2 MR and 1 SD, and PFS of 3 to 4 months. None had re-expansion of CART-BCMA cells. Non-specific immune modulation was observed and included altered CD4:CD8 T cell ratio (n=5), increased NK cell/decreased T cell frequency (n=4), and HLA-DR upregulation on CAR-negative T cells (n=2). More detailed phenotyping of CART and other immune cells, including PD-1 expression, is ongoing. With regard to toxicity, pt. 02 had self-limiting low-grade fevers and myalgias 4 weeks after pembro/pom/dex, associated with mild elevation in ferritin/CRP, suggestive of mild CRS. No other CRS was noted, including pt. 07 despite CART-BCMA re-expansion. One patient (17) developed recurrent expressive aphasia starting 2 months after elo/pembro/pom/dex, without signs of CRS and no observed expansion of CART-BCMA cells in blood or CSF. This resolved with stopping therapy and brief steroid taper.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that a PD1-inhibitor combination can induce CAR T cell re-expansion and anti-MM response in a MM patient progressing after CART-BCMA therapy. Since this patient previously progressed on pembro/pom/dex, the observed clinical activity was likely related to the CAR T cells, with elotuzumab also possibly contributing. However, this effect was very transient; re-expansion occurred infrequently (1/5 patients); and neurotoxicity was observed (though its relationship to the CAR T cells is unclear). This makes it difficult to endorse this specific salvage regimen. Nonetheless, this proof-of-principle observation suggests that a subset of patients may respond to checkpoint blockade or other immune-modulating approaches following BCMA CAR T cell therapy, meriting further study.
Garfall:Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Bioinvent: Research Funding. Melenhorst:novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Shanghai UNICAR Therapy, Inc: Consultancy; Casi Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy: Research Funding. Lacey:Parker Foundation: Research Funding; Tmunity: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Patents & Royalties; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Research Funding. Stadtmauer:Janssen: Consultancy; AbbVie, Inc: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy. Vogl:Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy. Plesa:Novartis: Research Funding. Young:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Levine:Novartis: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Tmunity Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Research Funding; Incysus: Consultancy; Cure Genetics: Consultancy; CRC Oncology: Consultancy; Brammer Bio: Consultancy. June:Immune Design: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Immune Design: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Tmunity Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Celldex: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Tmunity Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Milone:Novartis: Patents & Royalties. Cohen:Bristol Meyers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Poseida Therapeutics, Inc.: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Oncopeptides: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.